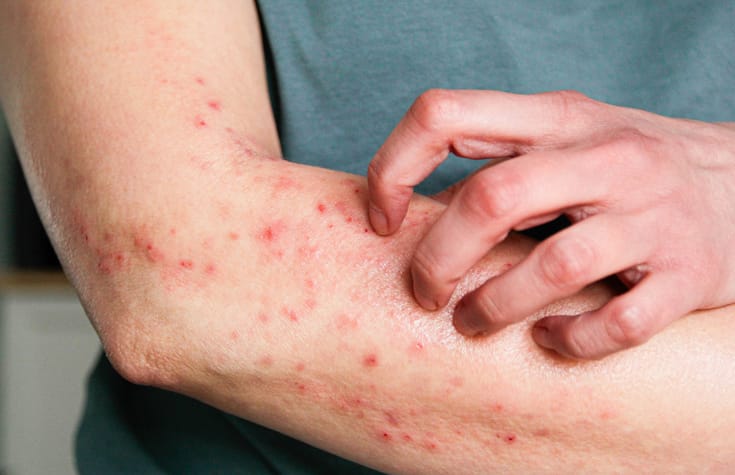
Skin reactions or irritations such as itching, flushing and hives are common symptoms in patients with systemic mastocytosis (SM).
Close monitoring of triggers to avoid symptom episodes and the use of antihistamines and topical skin treatments can help manage the debilitating effects of itchy, red rashes and flushing of the face.
What is SM?
Systemic mastocytosis (SM) is a rare hematological disease characterized by mast cells that are overactive and accumulate in different parts of the body such as the bone marrow, liver, spleen, gastrointestinal tract and lymph nodes.
Regular monitoring of the skin can help evaluate the effectiveness of the chosen treatment and allow a patient to optimize his approach and track disease progression.
Read more about SM signs and symptoms
Skin-related symptoms of SM
In SM, mast cells proliferate uncontrollably and build up in the skin tissue and internal organs. When an allergic reaction is triggered by a sudden change in temperature, alcohol, spicy food, certain medications, pollen, strong perfume, emotional stress, physical exertion or an insect sting, the mast cells release histamines and chemicals into the bloodstream.
The skin reacts to the release of histamines, cytokines and other chemicals by developing a rash, by flushing red or by becoming unbearably itchy.
Some common skin irritations found in people with SM include the following.
- Flushing: When the face becomes very red.
- Urticaria pigmentosa: A rash of itchy, dark-colored bumps.
- Maculopapular skin lesions: Flat red areas with many small bumps.
- Hives: Itching that doesn’t stop and develops into raised red spots if scratched.
The importance of regular skin monitoring
It is important for you to schedule regular appointments with a dermatologist familiar with SM as part of your SM treatment plan. Your dermatologist will document the size, location, color and appearance of your skin irritations.
Any growth or changes to your skin, such as flare-ups, will need to be investigated. Watch for the following.
- Worsening symptoms: You may need to revise your lifestyle and diet choices if your skin reactions worsen or if your symptom episodes become more severe, last longer or are more frequent.
- Treatment effectiveness: Track the evolution of your itchiness, rashes and redness to fine-tune your medication schedule.
- Disease progression: See your dermatologist regularly to check your skin or look for any indications that your SM is progressing.
- Unrelated skin complications: As you focus on your skin reactions, don’t overlook the possibility that you may have skin issues unrelated to SM, such as skin cancer.
Manage your skin symptoms
Proactively avoid your known triggers and take antihistamines to reduce the number of symptom episodes.
You can also soothe and protect your skin if you wear natural fibers, avoid friction to your skin, cover up to protect your skin from the sun and use hypoallergenic skin care products such as moisturizers to keep your skin hydrated.
Sign up here to get the latest news, perspectives and information about SM sent directly to your inbox. Registration is free and only takes a minute.